Reading Achievement
In 2003, the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) conducted a national reading assessment of fourth- and eighth-grade students. In the figures below, student performance is described by average scores on the NAEP reading composite scale, which ranges from 0 to 500. The national results reflect the performance of students attending both public and nonpublic schools. In addition to national results, the 2003 assessment collected performance data for fourth- and eighth-graders who attended public schools in all 50 states and three other jurisdictions that volunteered to participate.
The results presented in the figures and tables throughout this report distinguish between two different reporting samples that reflect a change in administration procedures. The more recent results are based on administration procedures in which testing accommodations (e.g., extended time, small group testing) were permitted for students with disabilities and limited-English-proficient students. Accommodations were not permitted in 1992 or 1994. Comparisons between results from 2003 and those from assessment years in which both types of administration procedures were used (in 1998 and 2000 at grade 4 and in 1998 at grade 8) are discussed based on the results when accommodations were permitted, even though significant differences in results when accommodations were not permitted may be noted in the figures and tables.
No significant change was detected between 2002 and 2003 in the average score for fourth-graders (figure 1). The average fourth-grade score in 2003 was not found to differ significantly from that in 1992. The average reading score for eighth-graders decreased by 1 point between 2002 and 2003; however, the score in 2003 was higher than that in 1992. (Differences are discussed in this report only if they were found to be statistically significant.)
Figure 1.?Average Fourth- and Eighth-Grade Reading Scores: 1992-2003
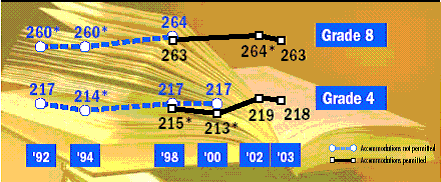
![]() Significantly different from 2003.
Significantly different from 2003.
NOTE: Average reading scores are reported on a 0-500 scale. Data were not collected at grade 8 in 2000. In addition to allowing for accommodations, the accommodations-permitted results at grade 4 (1998-2003) differ slightly from previous years' results, and from previously reported results for 1998 and 2000, due to changes in sample weighting procedures. Significance tests were performed using unrounded numbers.
SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences. National Center for Education Statistics. The Nation's Report Card Reading Highlights 2003, NCES 2004-452, by P. Donahue, M. Daane, and W. Grigg. Washington, DC: 2004.
The percentages of students performing at or above the Proficient1 level were higher in 2003 than in 1992 at both grades 4 and 8 (figure 2). No significant change was detected in the percentage of fourth-graders at or above Basic1 from 2002 to 2003, and the percentage of fourth-graders at or above Basic in 2003 was not found to differ significantly from that in 1992. The percentage of eighth-graders at or above Basic decreased by 1 point between 2002 and 2003, but was higher in 2003 than in 1992.
Figure 2 shows that 31 percent of fourth-graders and 32 percent of eighth-graders performed at or above the Proficient level in 2003. The percentage of students performing at or above the Basic level in 2003 was 63 percent at grade 4 and 74 percent at grade 8.
Figure 2. Percentages of students, by reading achievement level, grades 4 and 8: 1992-2003
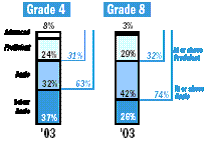
NOTE: Detail may not sum to totals because of rounding.
SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education. Institute of Education Sciences. National Center for Education Statistics. The Nation's Report Card Reading Highlights 2003, NCES 2004-452, by P. Donahue, M. Daane, and W. Grigg. Washington, DC: 2004.
_____________________
1 Achievement Levels:
Basic: This level denotes partial mastery of prerequisite knowledge and skills that are fundamental for proficient work at each grade.
Proficient: This level represents solid academic performance for each grade assessed.
Students reaching this level have demonstrated competency over challenging subject matter, including subject-matter knowledge, application of such knowledge to real-world situations, and analytical skills appropriate to the subject matter.
Advanced: This level signifies superior performance.