International Comparisons in Reading Literacy
The Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS) is an assessment of reading comprehension conducted by the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA). Thirty-five countries assessed the reading literacy of their students in the upper of two grades with the most 9-year-olds (fourth grade in most countries, including the United States). Data were collected in the final months of the 2000-01 school year. In the United States, data were collected in the spring of 2001 from both public and private schools.
PIRLS 2001 scores are reported on a scale of 0 to 1000, with an international average of 500 and a standard deviation of 100 1. For the 35 countries that participated in PIRLS 2001, figure 1 presents the average scores for the three scales: the combined reading literacy scale and its two components, the literary and informational subscales. U.S. fourth-grade students performed significantly better than the international average of 500 on the combined reading literacy scale. U.S. fourth-graders outperformed their counterparts in 23 of the 34 other countries participating in PIRLS 2001, although they scored lower than students in England, the Netherlands, and Sweden. No detectable differences in scores were found between U.S. students and their counterparts in eight of the remaining PIRLS 2001 countries. U.S. fourth-grade students performed better than the international averages on both of the reading subscales.
Figure 1. Fourth graders' average scores for the combined reading literacy scale, literary subscale, and informational subscale, by country: 2001
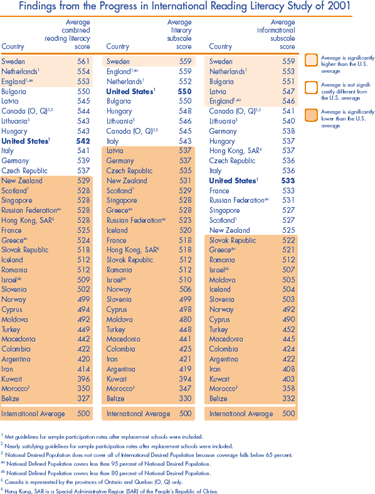
SOURCE: Figure 3 in U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. International Comparisons in Fourth-Grade Reading Literacy: Findings from the Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS) of 2001 (NCES 2003-073). Washington, DC.
1 The international average is the mean of all countries participating in the study calculated so that all participating countries have the same contribution to the average.