|
The
States, Districts and Territories of the United States
> American Samoa
|
|
 Flag |
 |
|
American Samoa
|
|
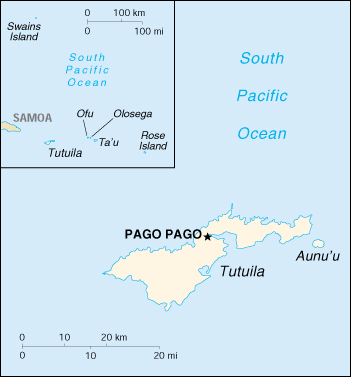
American Samoa is a group of five volcanic islands and two coral atolls located some 2,600 miles south of Hawaii in the South Pacific. It includes the eastern Samoan islands of Tutuila, Aunu'u, and Rose; three islands (Ta'u, Olosega, and Ofu) of the Manu'a group; and Swains Island. Settled as early as 1000 B. C., Samoa was "discovered" by European explorers in the 18th century. International rivalries in the latter half of the 19th century were settled by an 1899 treaty in which Germany and the US divided the Samoan archipelago. The US formally occupied its portion - a smaller group of eastern islands with the excellent harbor of Pago Pago - the following year. It is an unincorporated and unorganized territory of the US; administered by the US Department of the Interior. This is a traditional Polynesian economy; more than 90% of the land is communally owned. Economic activity is strongly linked to the US, with which American Samoa conducts the great bulk of its foreign trade. Tuna fishing and tuna processing plants are the backbone of the private sector, with canned tuna being the primary export. Attempts by the government to develop a larger and broader economy are restrained by Samoa's remote location, its limited transportation, and its devastating hurricanes. GOVERNMENT Population (2002 est.): 68,688; average rate of natural increase: 2.31% Land Area: 77 sq. mi (199 sq. km) ECONOMY |
|
DISCLAIMER Any reference obtained from this server to a specific commercial product, process, or service does not constitute or imply an endorsement by the United States Government of the product, process, or service, or its producer or provider. The views and opinions expressed in any referenced document do not necessarily state or reflect those of the United States Government. |
|
U.S. Diplomatic Mission to Germany
/Public Affairs/ Information Resource Centers Updated: June 2003 |